By Rishab Narang (Curated from CSI's Big Data Edition)
Big Data[1] is a large volume of data from various data sources such as social media, web, genomics, cameras, medical records, aerial sensory technologies, and information sensing mobile devices. Big Data includes structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. This unstructured data contains useful information which can be mined. Since 1980s, per-capital capacity to store information is increased into double the amount for every 40 months. In 2012, statistics says that 2.5 quintillion (2.5 * 218) bytes of data are created per day. Moreover, digital streams that individuals create are growing rapidly. For example, most of the people are using camera on their own. Big Data are of high level volume, high velocity, and high variety of information that needs advanced method to process the Big Data. In addition, conventional software tools are not capable of handling Big Data. So Big Data requires extensive architecture. The following types of data are referred to as big data. • Social data – Customer feedback forms for Customer Relationship Management (CRM) in Social media sites such as Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn etc. • Machine-generated data – Sensor readings, Satellite communication • Traditional enterprise data- Employee information, business product, purchase, sales, customer Information, and ledger information.
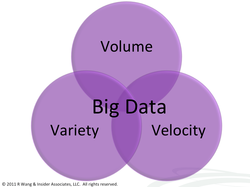
Traits of Big Data Big data diff ers from other data in 5 dimensions[3] such as volume, velocity, variety, and value. Volume: Machine generated data will be large volume of data. Velocity: Social media websites generates large data but not massive. Rate at which data acquired from the social web sites are increasing rapidly. Variety: Diff erent types of data will be generated when a new sensor and new services. Value: Even the unstructured data has some valuable information. So extracting such information from large volume of data is more considerable. Complexity: Connection and correlation of data which describes more about relationship among the data. Challenges Storing and Maintaining the Big Data is a challenging task. The following challenges need to be faced by the enterprises or media when handling Big Data: • Capture • Duration
• Storages • Search • Sharing • Analysis • Visualizations Why Big Data? Big Data is absolutely essential for the following intents: • To spot business trends • Determine quality of research • To prevent diseases • To link legal citation • To combat crime • T o determine real time roadway communication system, where the data is created in the order of exa bytes (218). Where it is used? Areas or fi elds where big data are created: • Medicine, Meteorology, Connectomics, Genomics, Complex Physics Simulation, Biological, Environment Research, and Areal Sensory System (remote sensing technologies). • Big Science, RFID, Sensor Networks. • Astrometry.net project keeps eye on Astrometry group via fl icker for new photos of the night sky. It analyzes each image and identifi es the celestial bodies such as stars, galaxies etc.
MapReduce MapReduce[2] is a programming model for handling complex combination of several tasks and it was published by Google. It is a batch query processor and can run an ad hoc query for whole dataset and get the results in a sensible manner which has to be transformative. It has two steps. 1. Map: Queries are divided into sub queries and allocated to several nodes in the distributed system and processed in parallel. 2. Reduce: Results are assembled and delivered.
Database Oracle has introduced the total solution for the scope of enterprise which requires Big Data. Oracle Big Data Appliance[3] is a tool to integrate optimized hardware and extensive software into Oracle Database 11g to endure the Big Data challenges. Example Application: Patient Health Information System on Cloud The Real-time application of Big Data can also be in Patient Health Information System on Cloud[4]. Patient Health Record (PHR) is an emerging technique to store the
Big Data
Patient Heath Information Record and exchange the data over the network, which is stored at the cloud for accessing the data
log anytime and anywhere. To assure more security individuals are given with their own login and data stored over the cloud would be encrypted. PHR includes variety of data such as structured, unstructured, and semi- structured.
• In PHR, we propose machine generated data by acquiring the finger print or iris pattern or face of the patient for saving the entire data log of the patient. It uses finger print sensor or Iris scanner or face recognizer for capturing the patient Identification. Finger print or iris pattern or facial expression act as a key for retrieving the data saved in the database
• Traditional enterprise data includes the entire PHR right from his/her birth with the details of the doctors and their prescription and all records.
• PHR called as social data which can be made online for online consultation and medicine purchase. Even the lab test reports can be uploaded online. This avoids patient waiting time in the lab for the result report. A copy of the result report will also be sent to the respective consulting doctor for further enquiry. An individual login is provided for patient, doctor, pathologist, pharmacists, etc. , which makes the system more secure.
Conclusion Omar Tawakol, CEO, Bluekai has written an article recently. In that article, he has mentioned that “More data usually beats better algorithm”. But it is very rigid to store and analyze. However, Big Data are used for finding the customer behavior, for identifying the market trends, for increasing the innovations, for retaining the customers, for performing the operations effiwociently. Flood of data coming from many sources must be handled using some non-traditional database tools. It provides more market value and systematic for the upcoming generation.
Traits of Big Data Big data diff ers from other data in 5 dimensions[3] such as volume, velocity, variety, and value. Volume: Machine generated data will be large volume of data. Velocity: Social media websites generates large data but not massive. Rate at which data acquired from the social web sites are increasing rapidly. Variety: Diff erent types of data will be generated when a new sensor and new services. Value: Even the unstructured data has some valuable information. So extracting such information from large volume of data is more considerable. Complexity: Connection and correlation of data which describes more about relationship among the data. Challenges Storing and Maintaining the Big Data is a challenging task. The following challenges need to be faced by the enterprises or media when handling Big Data: • Capture • Duration
• Storages • Search • Sharing • Analysis • Visualizations Why Big Data? Big Data is absolutely essential for the following intents: • To spot business trends • Determine quality of research • To prevent diseases • To link legal citation • To combat crime • T o determine real time roadway communication system, where the data is created in the order of exa bytes (218). Where it is used? Areas or fi elds where big data are created: • Medicine, Meteorology, Connectomics, Genomics, Complex Physics Simulation, Biological, Environment Research, and Areal Sensory System (remote sensing technologies). • Big Science, RFID, Sensor Networks. • Astrometry.net project keeps eye on Astrometry group via fl icker for new photos of the night sky. It analyzes each image and identifi es the celestial bodies such as stars, galaxies etc.
MapReduce MapReduce[2] is a programming model for handling complex combination of several tasks and it was published by Google. It is a batch query processor and can run an ad hoc query for whole dataset and get the results in a sensible manner which has to be transformative. It has two steps. 1. Map: Queries are divided into sub queries and allocated to several nodes in the distributed system and processed in parallel. 2. Reduce: Results are assembled and delivered.
Database Oracle has introduced the total solution for the scope of enterprise which requires Big Data. Oracle Big Data Appliance[3] is a tool to integrate optimized hardware and extensive software into Oracle Database 11g to endure the Big Data challenges. Example Application: Patient Health Information System on Cloud The Real-time application of Big Data can also be in Patient Health Information System on Cloud[4]. Patient Health Record (PHR) is an emerging technique to store the
Big Data
Patient Heath Information Record and exchange the data over the network, which is stored at the cloud for accessing the data
log anytime and anywhere. To assure more security individuals are given with their own login and data stored over the cloud would be encrypted. PHR includes variety of data such as structured, unstructured, and semi- structured.
• In PHR, we propose machine generated data by acquiring the finger print or iris pattern or face of the patient for saving the entire data log of the patient. It uses finger print sensor or Iris scanner or face recognizer for capturing the patient Identification. Finger print or iris pattern or facial expression act as a key for retrieving the data saved in the database
• Traditional enterprise data includes the entire PHR right from his/her birth with the details of the doctors and their prescription and all records.
• PHR called as social data which can be made online for online consultation and medicine purchase. Even the lab test reports can be uploaded online. This avoids patient waiting time in the lab for the result report. A copy of the result report will also be sent to the respective consulting doctor for further enquiry. An individual login is provided for patient, doctor, pathologist, pharmacists, etc. , which makes the system more secure.
Conclusion Omar Tawakol, CEO, Bluekai has written an article recently. In that article, he has mentioned that “More data usually beats better algorithm”. But it is very rigid to store and analyze. However, Big Data are used for finding the customer behavior, for identifying the market trends, for increasing the innovations, for retaining the customers, for performing the operations effiwociently. Flood of data coming from many sources must be handled using some non-traditional database tools. It provides more market value and systematic for the upcoming generation.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed